Rasa Kibana Dashboard
In this post, I’ll be using Ubuntu and Docker to setup an Elastic (ELK) stack to display a Kibana dashboard showing activity of a Rasa bot. We’ll forward the Rasa bot activity to ELK by via a Rasa event broker queue.
Apr 5, 2020: Updated Kibana dashboard gist
This post assumes you are using Rasa with the standard docker-compose setup which uses RabbitMQ. I’m using the Logstash RabbitMQ input plugin to grab the Rasa tracker store. I’m also going to assume that Rasa & ELK are on the same system. In most situations, this would not be the case so you would also install Logstash on your Rasa system and direct it send messages to the ELK server.
What’s Elastic and ELK
ELK is the acronym for three open source projects: Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. We’ll use these to generate this basic Rasa status dashboard.
Install & Start ELK
An easy way to get the ELK stack up and running is to use Docker with docker-compose and the deviantony docker-elk setup.
git clone https://github.com/deviantony/docker-elk
sudo chown -R 1000:1000 docker-elk/
cd docker-elk
You can change the default password, changeme, in the following files:
emacs docker-compose.yml kibana/config/kibana.yml logstash/config/logstash.yml elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml logstash/pipeline/logstash.conf
Let’s also change the license type from trial to basic by editing this value in elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:
xpack.license.self_generated.type: trial
Run docker-compose to start the ELK stack:
sudo docker-compose up -d
Verify ELK is Up
You can use curl to verify the login to Elastic:
curl -u elastic:rasa http://elasticsearch:9200/_security/_authenticate
You should now be able to access the Kibana web UI at port 5601 and login as the user elastic with the changeme password. Note that Kibana can take a few minutes to start. During this time you’ll see the message “Kibana server is not ready” when you browse to the homepage
Ports:
| Port | Use |
|---|---|
| 9200 | ElasticSearch |
| 9300 | ElasticSearch |
| 5601 | Kibana web UI |
| 5000 | Logstash beat service |
| 9600 | Logstash monitoring API |
Generate Passwords
This is described in more detail here. To secure your ELK stack, run the following commands and save the passwords that are generated.
sudo docker-compose exec -T elasticsearch bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords auto --batch
In the kibana/config/kibana.yml change the elasticsearch username to kibana with the newly generated password.
In the logstash/config/logstash.yml file change the username to logstash_system and update the password.
Replace the password for the elastic user in logstash/pipeline/logstash.conf.
emacs docker-compose.yml kibana/config/kibana.yml logstash/config/logstash.yml elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml logstash/pipeline/logstash.conf
Then re-start the kibana & logstash services:
sudo docker-compose restart kibana logstash
Use curl to verify the login to Elastic with the new password:
curl -u elastic:<new-password> http://localhost:9200/_security/_authenticate
Docker Monitoring (optional)
Log back into Kibana. Since we’re running Docker on the ELK system, you can quickly try out the Kibana docker monitoring. Click the Kibana icon in the upper left hand corner.
On the screen that is displayed, choose the Add metric data button and then choose Docker metrics from the list of available metric sources. Follow the steps presented and you’ll start seeing your docker metrics.
Start metricbeat with sudo service metricbeat start
If the timezone isn’t correct, choose Management > Advanced Settings tab and search for timezone.
Rasa Event Queue
If you are running Rasa X, you would normally have a Rabbit container running and the endpoints.yml will have an event_broker section that looks like this:
event_broker:
type: "pika"
url: ${RABBITMQ_HOST}
username: ${RABBITMQ_USERNAME}
password: ${RABBITMQ_PASSWORD}
queue: ${RABBITMQ_QUEUE}
The RabbitMQ event broker is used to foward the tracker events to Rasa X via a message queue named rasa_production_events
In the Rasa project home directory, edit the event_broker: section of the endpoints.yml and replace the queue: ${RABBITMQ_QUEUE} with the following. This creates a second queue called elk_log which will provide a copy of the tracker events for ELK.
queues:
- ${RABBITMQ_QUEUE}
- elk_log
If you are using Rasa X, you need to expose the RabbitMQ ports so Logstash can read the new queue. To do that, add the following to the rabbit: service in the docker-compose.override.yml:
rasax:
ports:
- "5672:5672"
- "15672:15672"
If you aren’t using Rasa X, you can start a RabbitMQ Docker container with this docker-compose fragment.
rabbit:
restart: always
image: "bitnami/rabbitmq:3.7.17"
environment:
RABBITMQ_HOST: "rabbit"
RABBITMQ_USERNAME: "user"
RABBITMQ_PASSWORD: ${RABBITMQ_PASSWORD}
RABBITMQ_DISK_FREE_LIMIT: "{mem_relative, 0.1}"
expose:
- "5672"
ports:
- "5672:5672"
- "15672:15672"
Restart Rasa for the event broker changes to take effect:
sudo docker-compose down
sudo docker-compose up -d
Talk to your bot to put some data into your tracker store and then check to make sure the new Rabbit queue has received the events. Here are some example http calls for RabbitMQ
curl -i -u user:password http://localhost:15672/api/overview
curl -i -u user:password http://localhost:15672/api/definitions
curl -i -u user:password http://localhost:15672/api/vhosts/%2F/connections
curl -i -u user:password http://localhost:15672/api/queues/%2F/elk_log
curl -i -u user:password -XPOST -d'{"count":1,"encoding":"auto","ackmode":"ack_requeue_true"}' http://localhost:15672/api/queues/%2F/elk_log/get
curl -i -u user:password -XPOST -d'{"count":1,"encoding":"auto","ackmode":"ack_requeue_true"}' http://localhost:15672/api/queues/%2F/rasa_production_events/get
Setup Logstash RabbitMQ Reader
The Logstash Rabbitmq input plugin allows us to read the elk_log queue we create in the Rasa endpoint. There’s an example post on this integration that I found helpful here. There’s a more detailed intro to Logstash here.
Go to your docker-elk home directory and edit the logstash/pipeline/logstash.conf file. Update passwords and insert rabbitmq input configuration block.
| logstash_1 | [2020-06-13T17:13:01,059][ERROR][logstash.inputs.rabbitmq ][main] RabbitMQ connection error, will retry. {:error_message=>”Connection refused: target host unknown (cannot be resolved). Target host list: |
input {
rabbitmq {
queue => "elk_log"
host => "<host ip addr>"
port => 15672
user => "user"
password => "<rabbit user password>"
durable => true
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["elasticsearch:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "<elastic password>"
}
}
filter {
if [@metadata][rabbitmq_properties][timestamp] {
date {
match => ["[@metadata][rabbitmq_properties][timestamp]", "UNIX"]
}
}
}
After changing the Logstash config, restart the docker-elk stack: sudo docker-compose restart. Review the logstash output to make sure it is connecting to RabbitMQ - sudo docker-compose logs -f logstash.
Kibana Setup
Go to the Stack Monitoring page in Kibana and click on the Logstash overview to see if you have received Rasa tracker events.
When logstash messages have arrived go to Management > Index Patterns and create an index pattern for logstash-* and specify @timestamp as the time filter field. You should now be able to go to Discover > logstash and view your messages.
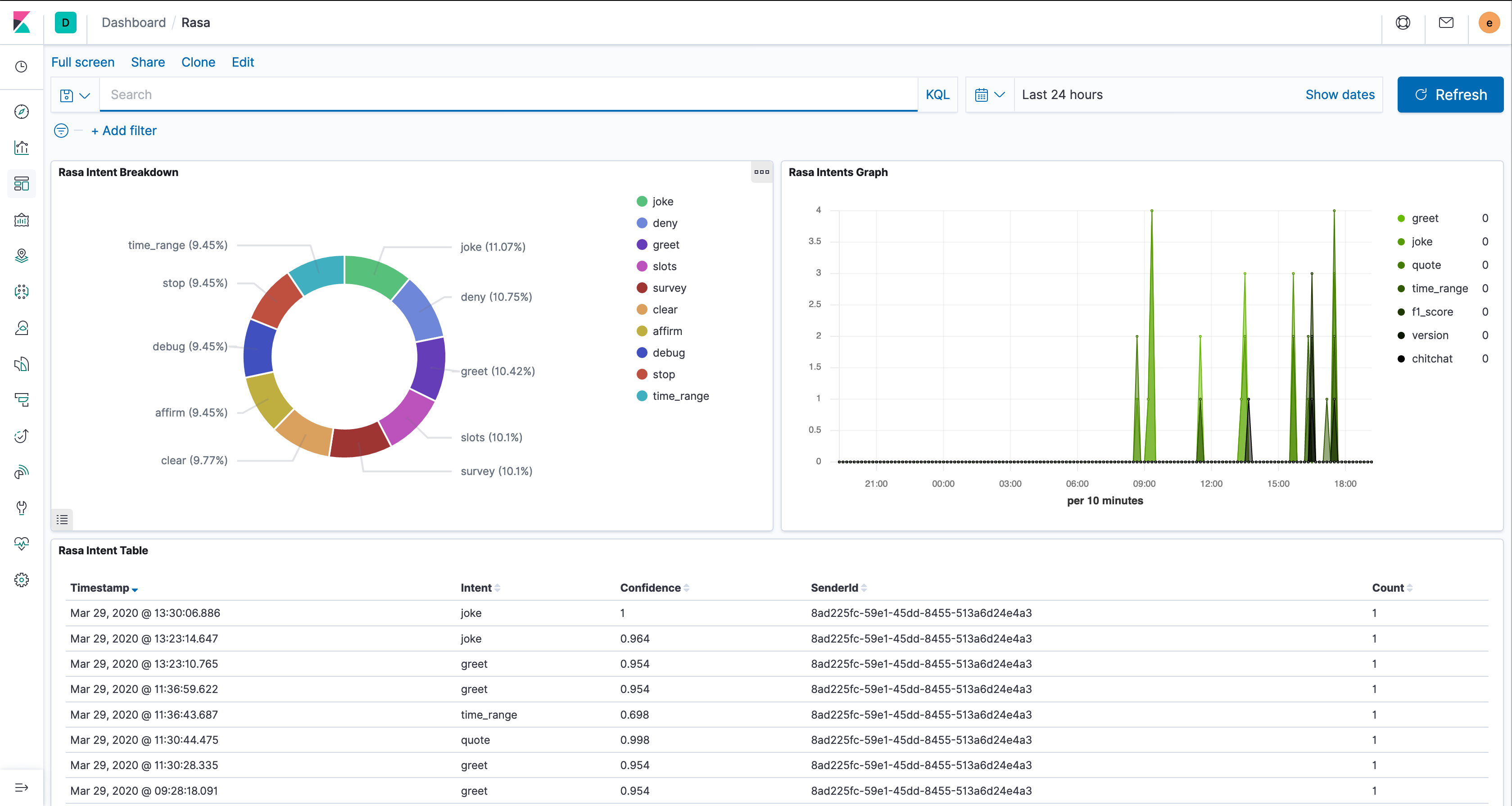
Rasa Dashboard
To import the sample Rasa dashboard, go to Management > Saved Objects > Import and import the file rasa_export.ndjson file.